Understanding the Versatility of Brass Ball Valves in Modern Flow Control
In the world of fluid control systems, brass ball valves stand as a testament to engineering excellence and practical functionality. These essential components play a crucial role in controlling liquid and gas flow across numerous industries, from residential plumbing to industrial processing. Their robust construction, reliability, and cost-effectiveness have made brass ball valves the preferred choice for professionals and homeowners alike.
The widespread adoption of brass ball valves can be attributed to their exceptional durability and resistance to corrosion, particularly in water-based applications. Their simple yet effective quarter-turn operation mechanism ensures quick and precise flow control, while their metal composition provides long-lasting performance under various pressure and temperature conditions.
Essential Components and Design Features
Core Construction Elements
At the heart of every brass ball valve lies a spherical ball with a bore through its center, precisely machined to ensure smooth operation and reliable sealing. The ball itself is typically crafted from brass or chrome-plated brass, offering excellent resistance to wear and corrosion. The valve body, also made from high-quality brass, houses the ball and provides connection points for the system.
The sealing mechanism consists of PTFE (Teflon) seats that create a tight seal against the ball, preventing leakage and ensuring consistent performance. These seats are designed to withstand repeated use while maintaining their integrity, making brass ball valves highly reliable for long-term applications.
Operating Mechanism Insights
The quarter-turn operation of brass ball valves represents one of their most significant advantages. This simple yet effective mechanism allows operators to quickly switch between fully open and fully closed positions with minimal effort. The stem, which connects the handle to the ball, is engineered with precision to ensure smooth rotation and prevent leakage around the stem seal.
Modern brass ball valves often incorporate additional features such as blow-out proof stems, adjustable packing glands, and anti-static devices for enhanced safety and performance. These design elements contribute to the valve's overall reliability and make it suitable for a wide range of applications.
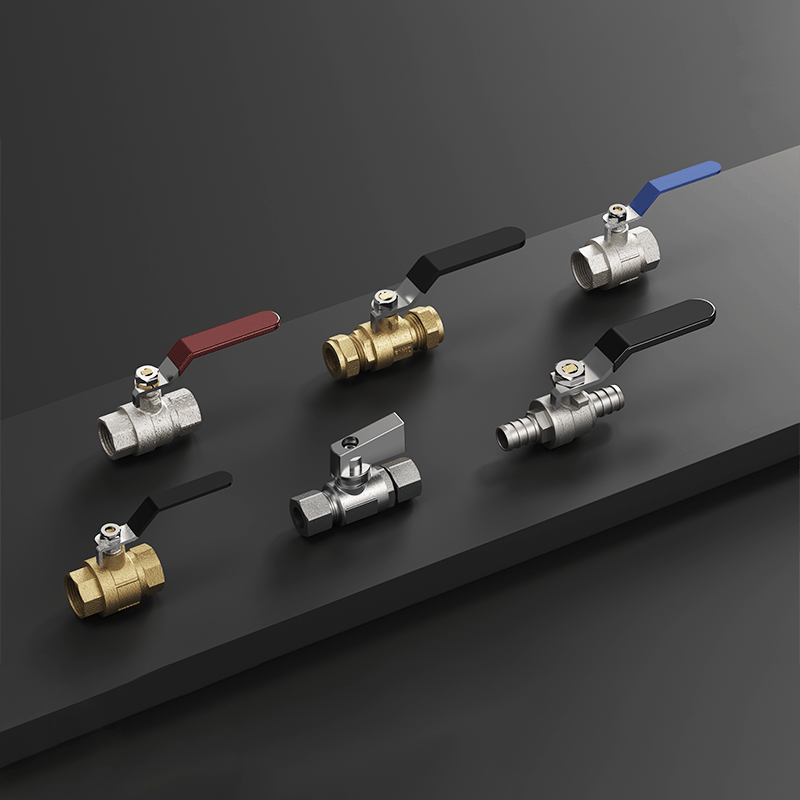
Size Classifications and Selection Criteria
Common Size Ranges
Brass ball valves are available in various sizes to accommodate different flow requirements and installation specifications. The most common sizes range from 1/4 inch to 4 inches in nominal diameter, with each size designed to handle specific flow rates and pressure ratings. Smaller valves (1/4 to 1 inch) are typically used in residential and light commercial applications, while larger sizes are reserved for industrial processes.
When selecting a brass ball valve size, considerations must include not only the pipe diameter but also the flow coefficient (Cv value), which indicates the flow capacity through the valve. This value becomes particularly important in applications where precise flow control is essential.
Pressure and Temperature Specifications
Different size classifications of brass ball valves come with varying pressure ratings, typically ranging from 150 PSI to 600 PSI for standard models. The maximum working pressure often depends on both the valve size and the operating temperature. As temperatures increase, the maximum allowable working pressure generally decreases according to specific temperature-pressure curves provided by manufacturers.
Temperature capabilities of brass ball valves typically range from -20°F to 400°F (-29°C to 204°C), though these values can vary based on the specific design and materials used in the valve construction. It's crucial to select a valve size that can handle both the required pressure and temperature specifications of the intended application.
Applications Across Industries
Residential and Commercial Usage
In residential settings, brass ball valves are commonly found in water supply systems, heating systems, and garden irrigation setups. Their reliability and ease of operation make them ideal for main water shutoff valves, fixture isolation valves, and appliance connections. The corrosion resistance of brass makes these valves particularly suitable for potable water applications.
Commercial buildings utilize brass ball valves extensively in their plumbing and HVAC systems. From controlling water flow in cooling towers to managing distribution in fire suppression systems, these valves prove their versatility in maintaining building services. Their durability and minimal maintenance requirements make them cost-effective choices for property managers.
Industrial Process Applications
Industries rely on brass ball valves for various process control applications, particularly in environments where corrosion resistance is crucial. Chemical processing plants use these valves for handling mild chemicals and water-based solutions. Food and beverage manufacturing facilities often choose brass ball valves for their sanitary properties and ability to maintain product purity.
The petroleum and natural gas industries also utilize brass ball valves in specific applications, especially in auxiliary systems where their pressure ratings and temperature capabilities meet the required specifications. Their quick-acting nature makes them valuable in emergency shutoff situations.
Maintenance and Performance Optimization
Regular Inspection Protocols
Maintaining brass ball valves requires periodic inspection of key components to ensure optimal performance. Regular checks should include examining the valve body for signs of corrosion, verifying smooth operation of the handle, and inspecting seals for any signs of wear or leakage. It's recommended to operate valves that are normally in one position (either open or closed) at least quarterly to prevent seizing.
Documentation of maintenance activities helps track valve performance over time and can indicate when replacement might be necessary. This proactive approach to maintenance can significantly extend the service life of brass ball valves and prevent unexpected failures.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When problems arise with brass ball valves, they typically manifest as leakage around the stem, difficulty in operation, or incomplete shutoff. Stem leaks can often be resolved by tightening the packing nut, while operation issues might require cleaning or lubricating the ball and seats. In cases of incomplete shutoff, debris caught between the ball and seats may need to be flushed out.
For valves exposed to harsh environments or frequent operation, implementing a preventive maintenance schedule can help identify potential issues before they lead to failure. This might include periodic cleaning, lubrication, and testing of valve operation under normal working conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes brass ball valves superior to other valve types?
Brass ball valves offer several advantages including excellent corrosion resistance, quick quarter-turn operation, reliable sealing, and cost-effectiveness. Their simple design results in minimal maintenance requirements and long service life, making them ideal for various applications.
How often should brass ball valves be maintained?
Regular maintenance should be performed at least annually, with more frequent inspections in critical applications. Valves that remain in one position should be operated quarterly to prevent seizing, while visual inspections for leaks or corrosion should be conducted monthly in industrial settings.
What is the typical lifespan of a brass ball valve?
Under normal operating conditions and with proper maintenance, brass ball valves can last 15-20 years or more. However, factors such as frequency of operation, environmental conditions, and quality of the installation can significantly impact their service life.
Can brass ball valves be used with hot water systems?
Yes, brass ball valves are suitable for hot water systems and can typically handle temperatures up to 400°F (204°C). However, it's important to verify the specific temperature rating of the valve and ensure it meets the system requirements, as pressure ratings may decrease at higher temperatures.




